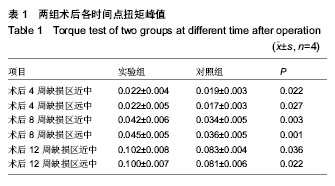
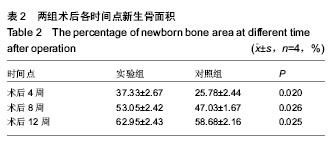
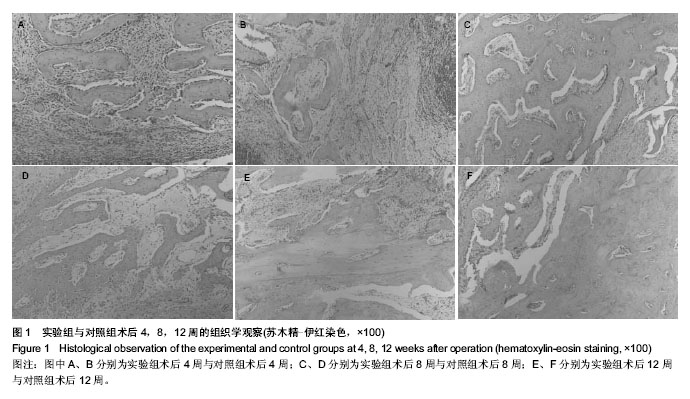
| [1] Ntounis A, Geurs N, Vassilopoulos P,et al.Clinical Assessment of Bone Quality of Human Extraction Sockets After Conversion with Growth Factors.Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2014.doi: 10.11607/jomi.3518. [Epub ahead of print]
[2] Mogharehabed A,Birang R,Torabinia N,et al.Socket preservation using demineralized freezed dried bone allograft with and without plasma rich in growth factor: A canine study. Dent Res J (Isfahan).2014;11(4):460-468.
[3] Lekovic V,Milinkovic I,Aleksic Z. Platelet-rich fibrin and bovine porous bone mineral vs. platelet-rich fibrin in the treatment of intrabony periodontal defects. J Periodontal Res.2012;47: 409-417.
[4] Sammartino G,Dohan Ehrenfest DM,Carile F.Prevention of hemorrhagic complications after dental extractions into open heart surgery patients under anticoagulant therapy: the use of leukocyte- and platelet-rich fibrin. J Oral Implantol. 2011;37: 681-690.
[5] Sunitha RV, Munirathnam NE.Platelet-rich fibrin: evolution of a second generation platelet concentrate.J Dent Res.2008; 19(1): 42-46.
[6] 鄂玲玲,王东胜,刘洪臣,等.一种新型的兔牙槽骨缺损模型的建立[J].中华老年口腔医学杂志,2011,9(3):137-140.
[7] Lee JW, Kim SG, Kim JY. Restoration of a peri-implant defect by platelet-rich fibrin. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol.2012;113:459-463.
[8] Almasri M,Altalibi M.Efficacy of reconstruction of alveolar bone using analloplastic hydroxyapatite tricalcium phosphate graft under biodegradable chambers.Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2011;49:469-473.
[9] Birang R, Torabi A, Shahabooei M,et al. Effect of plasma-rich in platelet-derived growth factors on peri-implant bone healing: An experimental study in canines. Dent Res J (Isfahan). 2012; 9:93-99.
[10] Novell J,Ivorra C,Munillla A,et al. Five-year result of implants inserted into freeze-dried block allograft.Implant Dent.2012; 21(2):129-135.
[11] Tang X,Yang SH,Xu WH,et al.Vertebral plate regeneration induced by radiation-sterilizeed allogeneic bone sheets in sheep.Clin J Traumatol.2007;1: 34-39.
[12] Malinin T,Thomas HT.Comparison of frozen and freeze-dried particulate bone allografts.Cryobiology.2007;2:167-170.
[13] Simonpieri A,Choukroun J,Del CM, et al. Simultaneous sinus-lift and implantation using microthreaded implants and leukocyte- and platelet-rich fibrin as sole grafting material:a six-year experience.Implant Dentistry.2011;20(1):2-12.
[14] Hiremath H,Saikalyan S,Kulkarni SS,et al.Second-generation platelet concentrate(PRF) as a pulpotomy medicament in a permanent molar with pulpitis:a case report.Int Endod J.2011; 45(1):105-112.
[15] Pradeep AR,Rao NS, Agarwal E.Comparative evaluation of autologous platelet-rich fibrin and platelet-rich plasma in the treatment of three-wall intrabony defects in chronic periodontitis: a randomized controlled clinical trial. J Periodontol. 2013; 83(12):1499-1507.
[16] Sharma A,Pradeep AR.Autologous platelet-rich fibrin in the treatment of mandibular degree II furcation defects: a randomized clinical trial. J Periodontol. 2011;82:1396-1403.
[17] Zhang Y, Tangl S, Huber CD. Effects of Choukroun's platelet-rich fibrin on bone regeneration in combination with deproteinized bovine bone mineral in maxillary sinus augmentation: a histological and histomorphometric study. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2012;40:321-328.
[18] Kim BJ, Kwon TK, Baek HS. A comparative study of the effectiveness of sinus bone grafting with recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein 2-coated tricalcium phosphate and platelet-rich fibrin-mixed tricalcium phosphate in rabbits. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol.2012;113: 583-592.
[19] Choukroun J,Adda F,Schoeffler C,et al.An opportunity in perioimplantology:The PRF.Implantodontie.2001;42:55-62.
[20] Choukroun J,Diss A,Simonpieri A,et al.Platelet-rich fibrin(PRF): a second-generation platelet concentrate.Part Ⅳ.Clinical effects on tissue healing. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod.2006;101(3):56-60.
[21] Dohan DM,Choukroun J,Diss A,et al.Platelet-rich fibrin(PRF): a second generation platelet concentrate. Part Ⅰ: technological concepts and evolution. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod.2006;101(3):37-44.
[22] Zumstein MA,Berger S,Schober M. Leukocyte- and platelet-rich fibrin (L-PRF) for long-term delivery of growth factor in rotator cuff repair: review, preliminary results and future directions. Curr Pharm Biotechnol.2012;13:1196–1206.
[23] Ozdemir H,Ezirganli S,Isa Kara M.Effects of platelet rich fibrin alone used with rigid titanium barrier. Arch Oral Biol.2013;58: 537-544.
[24] Peck MT, Marnewick J,Stephen L.Alveolar ridge preservation using leukocyte and platelet-rich fibrin: a report of a case. Case Rep Dent. 2011;2011:3450481.
[25] Charrier JB, Monteil JP, Albert S, et al. Relevance of Choukroun's platelet-rich fibrin(PRF) and SMAS flap in primary reconstruction after superficial or subtotal parotidectomy in patients with focal pleomorphic adenoma:a new technique. Rev Laryngol Otol Rhinol(Bord).2008; 129(4-5): 313-318.
[26] Dohan Ehrenfest DM,Bielecki T,Jimbo R. Do the fibrin architecture and leukocyte content influence the growth factor release of platelet concentrates? An evidence-based answer comparing a pure platelet-rich plasma (P-PRP) gel and a leukocyte- and platelet-rich fibrin (L-PRF).Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2012;13:1145-1152.
[27] Tatullo M,Marrelli M,Cassetta M,et al.Platelet-rich fibrin (PRF)in reconstructive surgery of atrophied maxillary bones: clinical and histological evaluations.Int J Med Sci.2012;9(10): 872-880.
[28] Landesberg R,Roy M,Glickman RS.Quantification of growth factor levels using a simplified method of platelet-rich plasma gel preparation. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2000;58(3):297-300.
[29] Visser LC,Arnoczky SP, Caballero O, et al. Platelet-rich fibrin constructs elute higher concentrations of transforming growth factor-β1 and increase tendon cell proliferation over time when compared to blood clots: a comparative in vitro analysis. Vet Surg.2010;39(7):811-817.
[30] Nacopoulos C,Dontas I,Lelovas P,et al. Enhancement of Bone Regeneration With the Combination of Platelet-Rich Fibrin and Synthetic Graft. J Craniofac Surg. 2014;25(6): 2164-2168. |